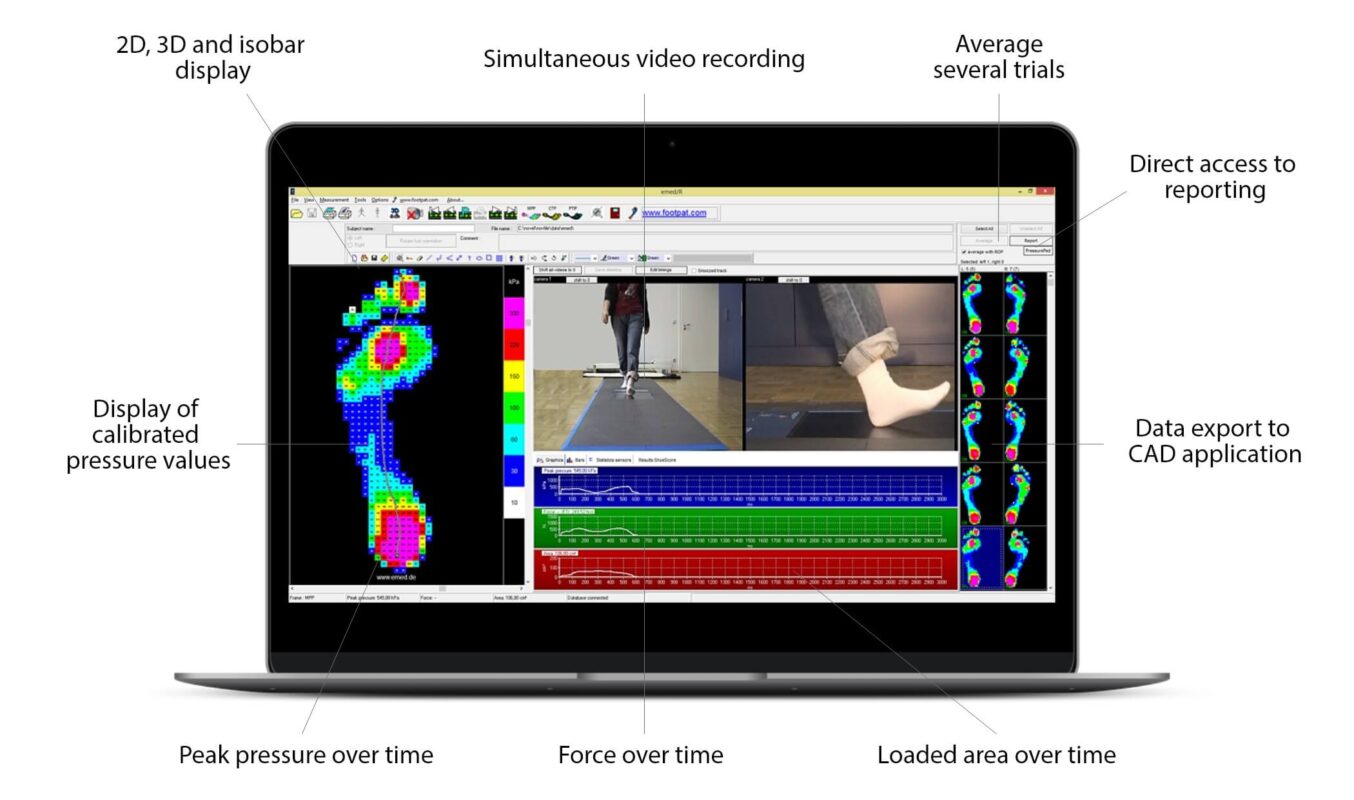
Applications:
1. Orthopedic Diagnoses
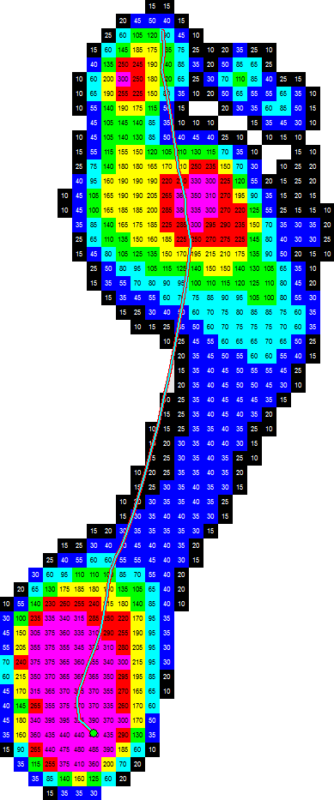
The emed system is a valuable tool in orthopedic diagnostics, providing detailed insights into foot pressure and gait mechanics. For example, it can detect abnormal pressure patterns in flatfoot (pes planus), where the arch support is lacking, leading to a more uniform pressure distribution. Conversely, in high arches (pes cavus), pressure is concentrated on the heel and forefoot. Additionally, the system identifies gait irregularities such as overpronation and supination, where the foot rolls inward or outward excessively during movement. This helps clinicians address biomechanical issues that may lead to chronic injuries. The system is also effective in diagnosing conditions like hallux valgus (bunion) by mapping pressure deviations caused by big toe misalignment, aiding in early intervention and treatment planning.
https://www.podiatric.theclinics.com/article/S0891-8422(23)00620-1/abstract
2. Diabetic Foot Care
In diabetic patients, early detection of high-pressure areas is vital to prevent foot ulcers. The emed system offers precise pressure mapping, enabling healthcare professionals to identify and monitor these areas effectively. This facilitates timely interventions, such as custom orthotics, to redistribute pressure and mitigate ulcer risk.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11415698/
3. Sports Medicine
Athletes benefit from the emed system’s ability to analyze foot pressure during dynamic activities. By identifying abnormal pressure distributions and gait patterns, the system aids in optimizing performance and preventing injuries through tailored training programs and corrective measures.
4. Post-Surgery Assessments
In post-surgical care, the emed system is invaluable for evaluating recovery and guiding rehabilitation. It monitors changes in pressure distribution and weight-bearing after procedures, helping clinicians assess whether the healing process is progressing as expected. For instance, it can identify if patients are placing excessive pressure on an operated foot, allowing adjustments to therapy or activity levels. This detailed feedback ensures that patients follow their rehabilitation protocols effectively, reducing the risk of complications and enhancing recovery outcomes.
5. Pediatric Diagnoses
The emed system is especially useful for diagnosing foot-related issues in children. It detects developmental abnormalities like pediatric flatfoot by analyzing pressure distributions and identifying the absence of an arch. This early detection allows for timely interventions, such as orthotics or physiotherapy, to correct the condition before it leads to long-term complications. Additionally, it can analyze gait abnormalities like toe-walking or uneven strides, providing actionable insights for tailored treatments that promote healthy foot development.
6. Rheumatologic Conditions
In rheumatologic care, the emed system provides crucial insights into how joint inflammation affects foot biomechanics. For example, in arthritis or rheumatoid foot deformities, the system captures changes in pressure distribution caused by joint damage. This data helps clinicians recommend appropriate interventions, such as supportive orthotics or specific therapies, to alleviate pain and improve mobility. By tailoring treatments to the patient’s unique needs, the emed system enhances the overall quality of care.
7. Neurological Disorders
For patients with neurological conditions like peripheral neuropathy or Parkinson’s disease, the emed system detects imbalances and abnormal pressure patterns. In neuropathy, the system helps identify areas of uneven weight distribution that increase the risk of falls. For Parkinson’s patients, it can track gait changes, such as shuffling or asymmetry, providing valuable data for designing gait training programs and fall prevention strategies. These insights contribute significantly to improving patient safety and mobility.
8. Elderly Foot Care
As people age, foot deformities like metatarsalgia or hammer toes become more common, often leading to pain and mobility issues. The emed system identifies pressure distribution changes associated with these conditions, helping clinicians design interventions to alleviate discomfort. It also assesses fall risks by highlighting imbalances in weight distribution and gait, allowing for targeted solutions like balance training or orthotic support to enhance the quality of life for elderly patients.
9. Custom Orthotic Design
Custom orthotics rely on precise pressure distribution data, which the emed system provides in detail. This information ensures that insoles or footwear are tailored to redistribute pressure effectively, addressing pain and correcting biomechanical issues. Whether for sports injuries, diabetic ulcers, or general foot discomfort, the system helps create orthotic solutions that enhance comfort and functionality, improving patient outcomes.
10. Obesity and Weight-Related Issues
Obesity often causes abnormal weight distribution, leading to increased pressure on specific foot areas, which can result in pain and structural deformities. The emed system maps these stress points, guiding interventions like weight redistribution insoles or targeted physiotherapy. It also tracks how gait changes with weight loss, helping clinicians monitor progress and adapt treatment plans accordingly.
These applications demonstrate the emed system’s versatility and effectiveness in enhancing diagnostic accuracy and patient care across various medical fields.